Cultivating Jute to be More Beneficial
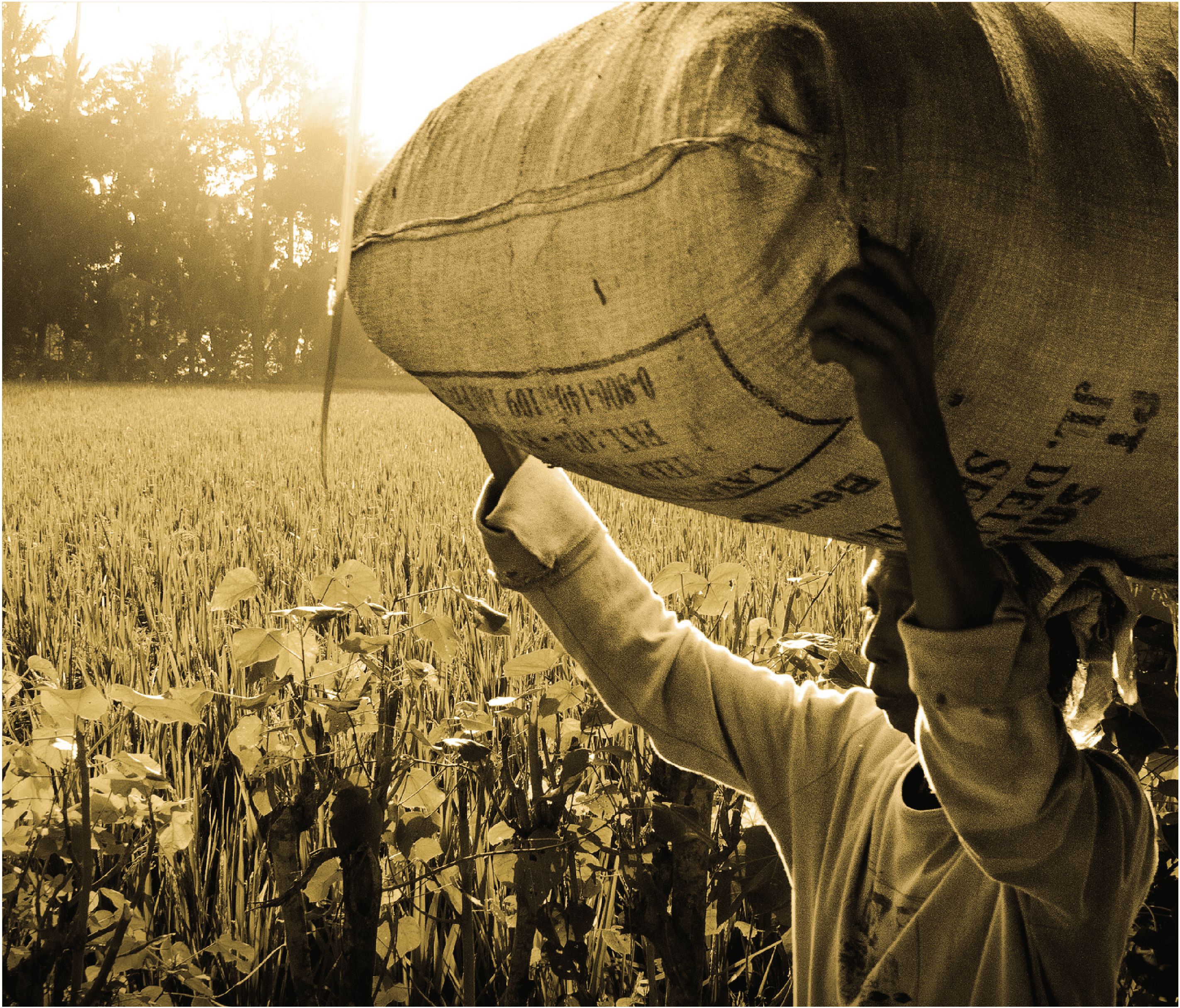

Talking about jute, everyone must have ever contacted with this thing. Material in the form of a brown sack dull and shabby, indeed, often be used for a number of goods or used to turn off the kerosene stove that exploded by watering it.
Jute does have a very low life cycle. After it becomes an unused wet finished sack, it turns into waste. If it is not stacked, jute will be thrown away or burned. In fact, jute is the result of factory pro- duction comes from natural fi- bers from plants Kenaf and Jute are manufactured by PT Perke- bunan Nusantara VIII. More- over, the production process of Jute is fairly massive and it is not easy. In fact, used jute sacks became alternative clothing for the people living in the colonial times of deprivation. But this time, nobody noticed jute waste due to the rapid development of soft material.
The Emerging of sacks materials made of synthetic fibers is believed to be one of the causes of reduced use of burlap sacks. Total production of jute sacks also declined, reached up 90,000 tons native fiber/year to only 60,000 tons of fibers/ year. In fact, one of the centers of production in the region Delanggu burlap sacks eventually liquidated.
Considering the number of used jute which only becomes waste, it is necessary to make the effort to the extent its life cycles a bit longer. Fibers from the jute sack that is no longer in good condition, need to be reconditioned to restore the structure of the fiber and recycled, thus it can generate new quality and useful textile material. How- ever, as the texture of threads on a sack, it is impossible to use it as raw fashion materials or clothing wear. Jute’s fiber is rough and itchy if it contacts with skin. But it is very possible if it is developed into a textile material as fashion accessories craft materials.
To that end, it has been conducted the survey of jute sack waste tested using the technique of single yarn and Non-Weaving Machine Tools weaving. But before it was conducted, it is needed to know the strengths and weaknesses of jute. Excellence jute is having porous fibers with good strength.
Moreover, in terms of functions, jute sacks are better than plastic sacks. However there are some disadvantages of jute, jute production is still low, while the value of sales was higher than plastic bags. Furthermore, the production of jute is still carried out semi marginal and needs very much time as well as more human source source to produce it while the plastic bag has been made marginal using heavy machinery. In addition, during this jute is produced just for taking of its primary function (sacks), but there is no consideration for the aesthetic side.
Improving Aesthetical Value of Jute
It is not easy to recondition jute, because of its shape and unattractive appearance. A dull brownish color, texture rough and hard, and when it is exposed to water, its damp will not be lost. To that end, before the experiment was done, jute goes into the preparation phase (preparation). After a Jute sack is separated into pieces of threads,
jute yarn. After this, there are two processes at the stage of preparation, namely scouring and bleaching.
The process of scouring is the fiber treatment process to remove impurities and omit the content of gum or sap on the surface of the fiber that causes fiber to handle so coarse and stiff. Through this process, the fiber will be softer and cleaner. In the process of scouring, jute is cooked by using water mixed with soda as liquid and Teepol in a certain period of time to get the most optimal fiber quality.
In this study, there are three recipes for jute scouring process. The first recipe uses 1.5 g / ltr as soda and 2.5 ml / ltr Teepol to cook 100 g kenaf fiber and 5 liters of water. The second recipe uses 5 g / ltr as soda and 5 ml / ltr Teepol to cook 100 g kenaf fiber and 5 liters of water. The Last recipe using 10 gr / ltr as soda and 10 ml / ltr Teepol to cook 100 g kenaf fiber and 5 liters of water. Each recipe is cooked for 30 minutes.
After scouring, jute fibers go into the bleaching process to change the dull color to white fibers. This process is actually optional in fiber processing. How- ever, the bleaching process is done in order to maximize fiber quality that will be colored.
In this study, the bleaching process is conducted to determine the capability of the fiber to absorb the color. In the bleaching process, there are two recipes that use. The first recipe using 2.5 ml / ltr H2O2 with 2.5 ml / ltr Na Silicate and 2.5 ml / ltr Teepol alongside 2.5 ltr of water and 100 grams of fiber. The second recipe using 5 ml / ltr H2O2 with 5 ml / ltr Na Silicate and 5 ml / ltr Teepol together 5 ltr water and 100 grams of fiber. Each recipe is cooked for 30 minutes.
After going through the process of scouring and bleaching, the resulted jute fibers are softer, clean, odorless, full white and tidier fiber structure.
The good quality Jute is then dried before going to the spinning stage using the technique of single yarn spinning and weaving on the handloom. In this study, experiments were conducted using a single yarn spinning which is manually using the jantra manual tool and handloom tool, because the scope of the test used is the only laboratory testing scope.
Not only that, the target of this study is Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), in which there are more people still use handloom. However, the use of spinning and weaving machines can only be done if the amount of production is very much and up tons and tons of fiber.
Based on the results of spinning, yarn produced has an inconsistent texture. Some threads are to be smaller, bumpy, and slightly larger because the yarn is spun manually only by the strength of the hand. However, this inconsistency makes jute yarn becomes more interesting in terms of aesthetics. There are three types of yarn obtained from the spinning: small, medium, and large yarn.
Then, the threads that have been woven enter the handloom weaving process. In the weaving process, there are three types of motives usually created; those are plain weave (plain weave), woven keeper (twill weave), and woven satin (satin weave). Plain weave is the simplest and often used to manufacture fabrics like calico, cotton, and canvas. In principle, the warp and weft yarns each interspersed one, resulting in a chessboard pattern structure. Woven keeper forms diagonal pattern characteristics on the surface of the fabric. To the left diagonal pattern is called “left keeper” and to the right is called “Right keeper”. Fabrics woven keeper is usually thicker than the other. For satin woven, in principle, warp yarns leap some woof at a time (4-11 thread), then passes the lower surface of the weft (1 time) and repeated. The shortcoming of this woven is, fabrics with the woven structures are more easily torn.
After it is woven, there will be six samples of fabrics with small different texture and shape loom, although all of them use a plain weave structure. All the six results of woven become different; it is not only the woven process techniques that tighten and loosen the woven yarn.
But also, the different size of twist in the yarn spinning process becomes one of the factors that make the characteristic woven vary. However, differences in texture and shape of each woven jute have an interesting aesthetic motif. Besides it is tested by using handloom, the threads of jute are experimented by crochet techniques. In this technique, jute yarn is knitted by a knitting tool, so that it can be a piece of cloth. This experiment proves the possibility of producing a new textile with different characteristics.
Based on research, jute waste still has an attractive point that can be innovated after it is processed. However, the fabrics structure produced cannot be used as fashion raw material, because it is still rough, even though it is not as rough as jute sacks.
However, the research is able to recommend jute waste development applied into something useful. By conducting many experiments mentioned above, the waste jute sacks can be recycled into a piece of aesthetic fabric.
Considering the jute fabrics characteristic produced, the future development that may be conducted is to implement jute fabrics as the textile craft raw material or fashion accessories. For instance, the jute fabrics can be used as the sheet of lamp cover, bag cover, shoe cover, belt cover, etc.
Although it has not reached the implementation stage, this research proved that jute sacks waste has a good chance to be recycled into a beneficial products in the future. It absolutely can enhance productivity, economical, and aesthetic value of jute. There should be further comprehensive research to identify the development of jute in the future. Whether it will be used as textile craft raw alternative material, as well as to find out the strength and jute quality level that has been through processed and it is added to the dyeing process in it.
Excerpted from the research : “Utilization of Jute Bag Waste Through the Experiment of Single Yarn and Weav- ing Handloom as Alternative Raw Materials for the Textile Handicraft Products “ by Dawn Ciptandi , S.Ds. , M.Ds. and Citra Puspitasari , S.Ds. , M.Ds.